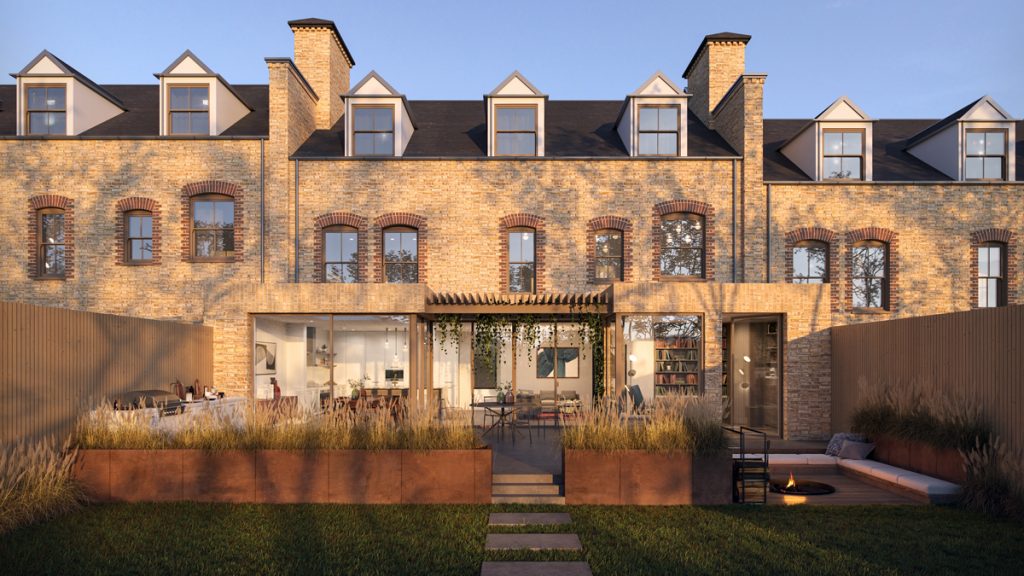
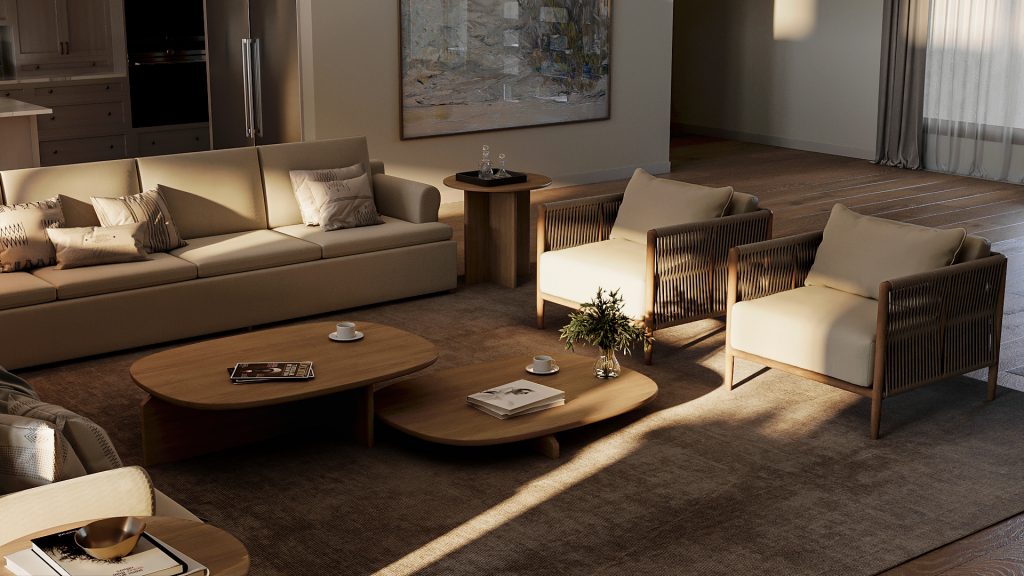
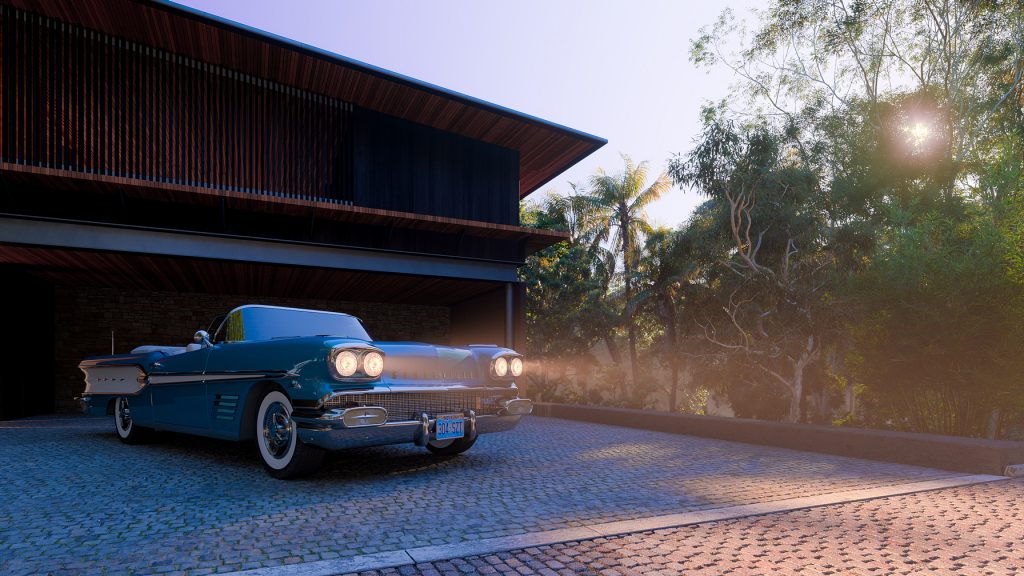
Light is not just a technical tool in 3D visualization, it is a tool that creates mood, volume, and life in every scene. Properly set up lighting can turn even the simplest model into an impressive, photorealistic picture. In this article, we’ll look at why light plays a key role in 3D visualization, what the main types of lighting are, and how, even without professional knowledge, you can set up a lighting scheme to make your scene look convincing and atmospheric. Ready to create your own story with light? Then let’s get going!